History of Infrastructure
The term infrastructure has been used throughout history to describe the large and complex structures of military projects, civil projects, and public utilities. The word was first used in 1875 in France to describe railroad planning. However, prior to the 1700s, what later became known as infrastructure began with roads and canals for transportation and irrigation. The 1800s through the early 1900s added railroad, telegraph, electrical, water/sewer, subway, and telephone communication infrastructure. As technology evolved from basic computing to the Internet and beyond, business operations quickly became dependent on technology. Over time, the IT infrastructure became a backbone of business.
Today the term is used to encompass the ever-growing foundations, structural components, and relationships of today’s integrated business frameworks. The term, taken from the French infra, means under or below. This highlights that a firm foundation is needed to support a strong organizational framework.
Below is a list of areas that are commonly referred to as infrastructure:
- Highways
- Streets/roads
- Bridges
- Airports
- Railroads
- Water utilities
- Electrical utilities
- Energy utilities
- Telecommunications
- Waste utilities
- Technology hardware, software, networks, facilities
What Is IT Infrastructure?
Today’s CIOs are tasked with efficiently operating the technology infrastructure that supports overall enterprise or corporate goals. Part of this responsibility includes increasing business value by streamlining information retrieval and reporting, providing proactive and agile responses to leverage information and technology, and quickly adapting to allow enhanced end user experiences. In order to accomplish this enormous undertaking, IT leadership relies on the myriad of tangible and intangible elements that make up the technology backbone of an organization, the IT infrastructure.
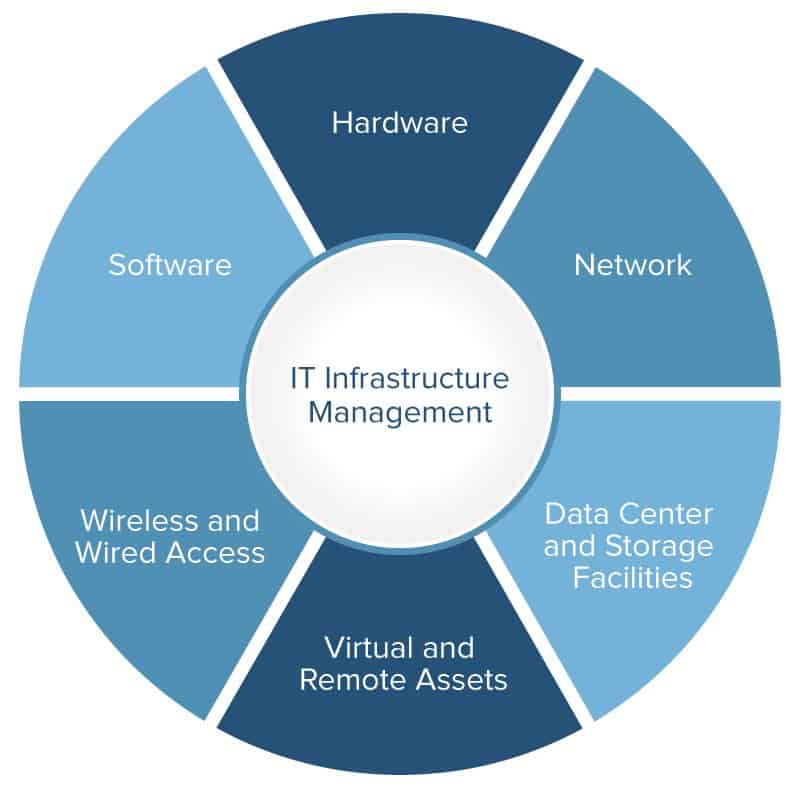
The IT infrastructure consists of all elements that support the management and usability of data and information. These include the physical hardware and facilities (including data centers), data storage and retrieval, network systems, legacy interfaces, and software to support the business goals of an enterprise. The structure also includes hiring, training, policy, testing, process, upgrades, and repairs.
What Is Infrastructure Management?
The term infrastructure describes the structures required for the operation of a physical facility or business operation. As mentioned earlier, infrastructure management has evolved to include the true backbone of business, technology. This is referred to as IT infrastructure management. The purpose of IT infrastructure management is to provide structure and control of the functions responsible for diverse technical operations which generally involve hardware, software, and networking in both physical and virtual environments. The main goal is to minimize downtime and maintain business productivity. Because of the complexity of IT infrastructure, it is not uncommon for IT infrastructure management to be broken into substructures, such as systems management, network management, and storage management.
Additionally, an enterprise IT infrastructure management team is typically responsible for the following essential IT elements and services:
- Asset lifecycle
- Capacity monitoring/planning
- Storage
- Network utilization
- Availability
- Energy consumption
- Environmental issues
- Facilities (including data center infrastructure management)
- Physical and virtual assets
- Wireless and wired network operations
- Hardware
- Software
- Security (malware/virus protection)
- Mobile connectivity
- Maintenance/service updates
The services that the IT infrastructure management team delivers are typically behind the scenes. They maintain the technology that supports the daily operations, such as Internet, email, and data accessibility. The team relies heavily on real or near real-time management and monitoring solutions in order to maintain productivity.
Understanding Remote Infrastructure Management
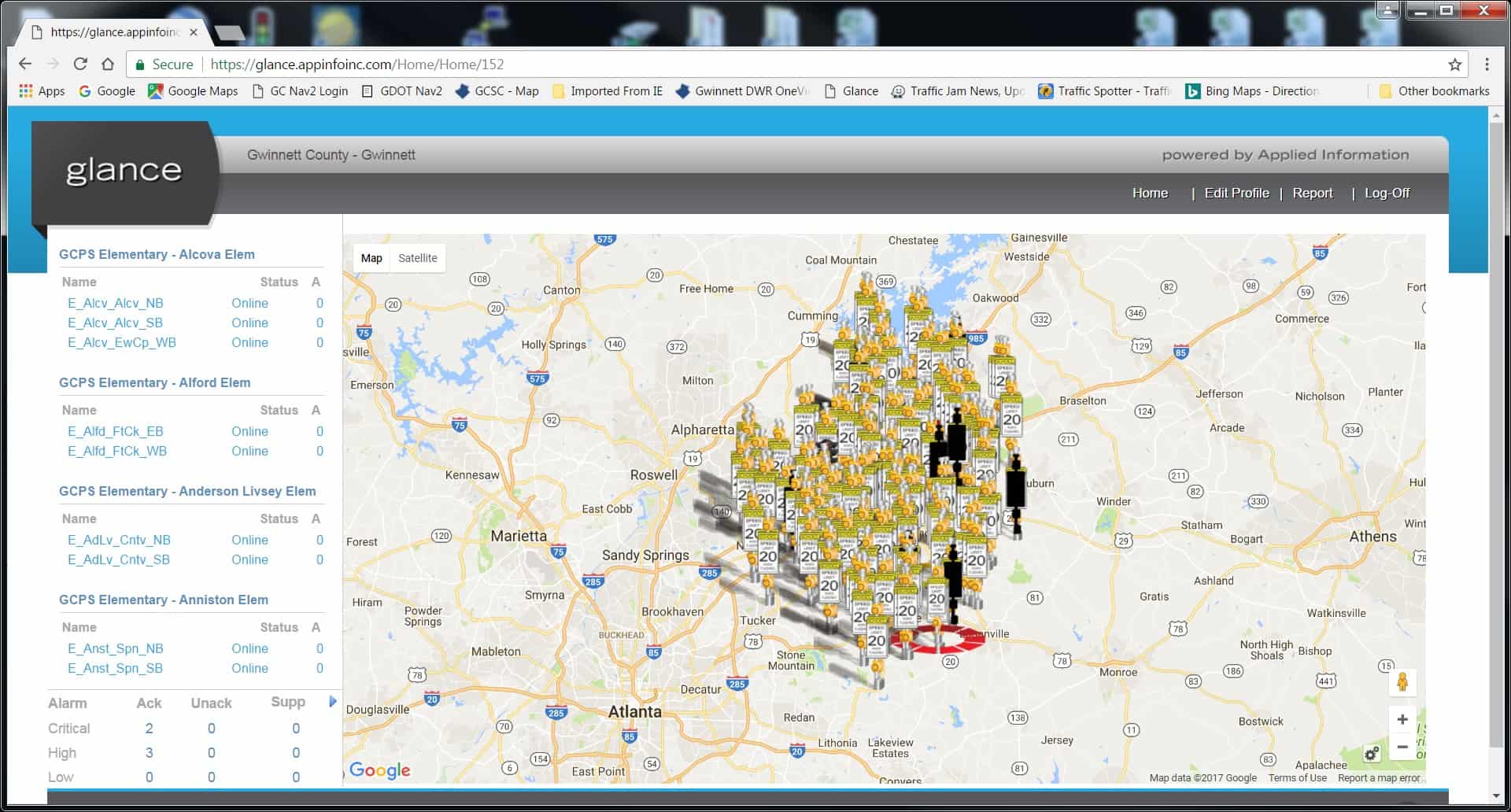
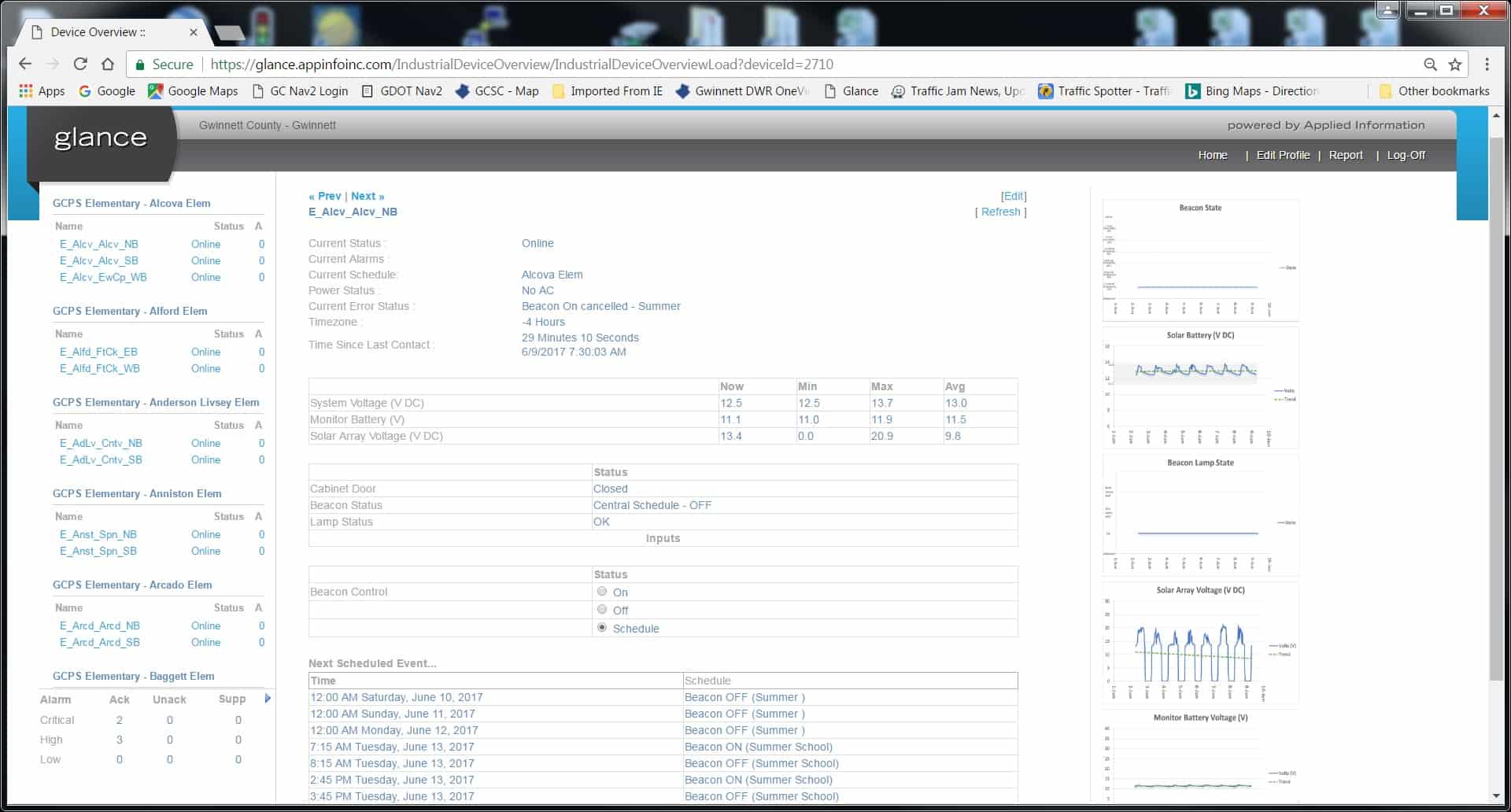
With the growing number of geographically disparate organizations, in addition to remote workers, cloud technology, and offsite data centers, Remote Infrastructure Management (RIM) helps with the centralized monitoring and management of these unique components that make up growing enterprises. RIM is managed by either in-house IT technicians or outsourced to IT service providers who have the tools and are versed in managing remote infrastructure.
The Gwinnett County Department of Transportation deploys a great example of infrastructure management that combines a public utility with technology and remote monitoring.
Infrastructure Project Manager
There are many technical and non-technical roles that make up an IT infrastructure management team. However, an Infrastructure Project Manager (IPM) has some unique responsibilities when it comes to managing infrastructure-specific projects, such as upgrades, integrations, and repairs. Infrastructure project management involves many of the general project management elements like planning, execution, monitoring, testing, and project closure. However, it is also highly technical: all projects are associated with maintaining the continual operation of the IT infrastructure. IPMs commonly have a variety of ongoing projects without defined end dates, whereas traditional PMs work on discrete projects with a final due date.
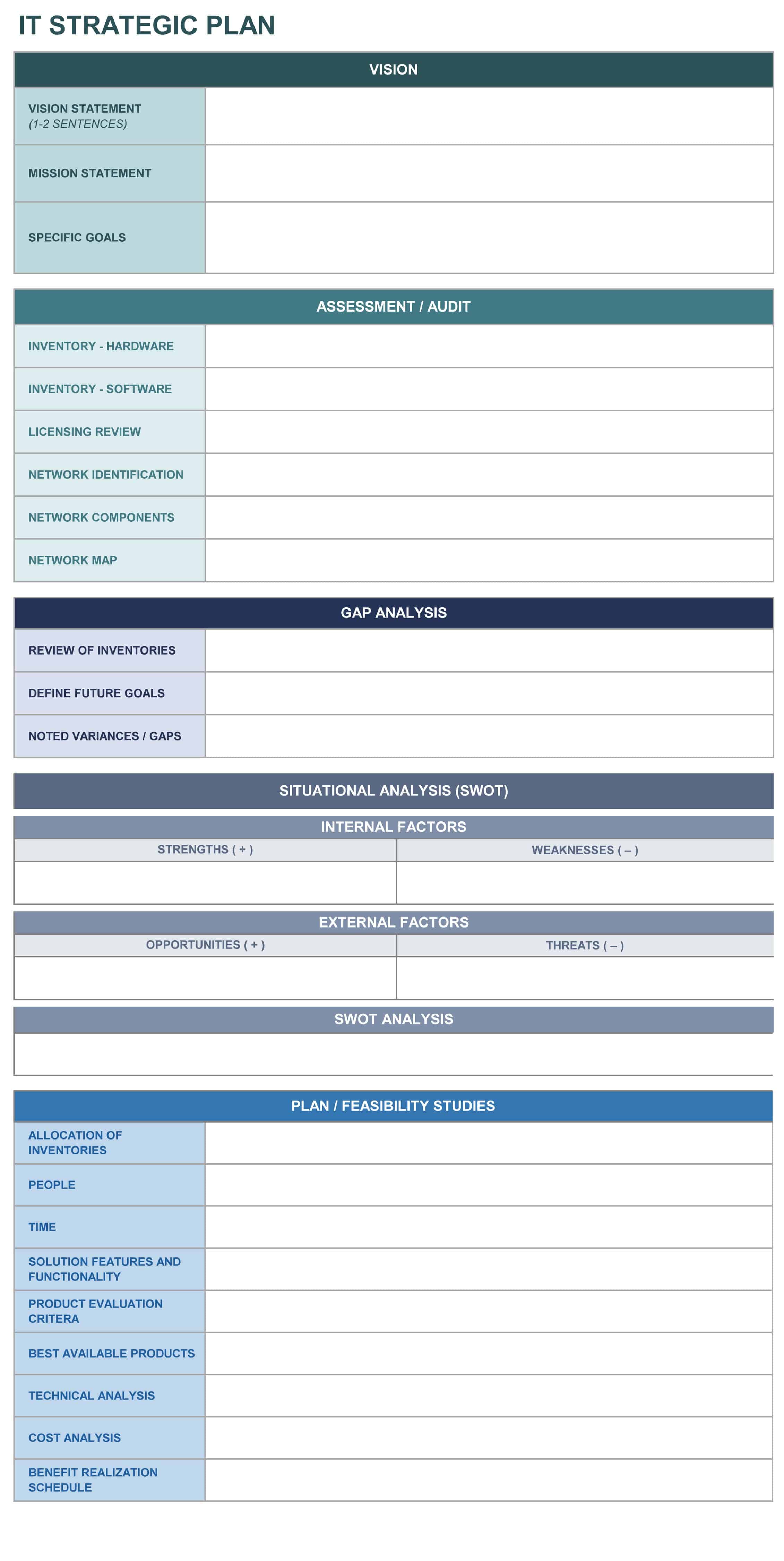
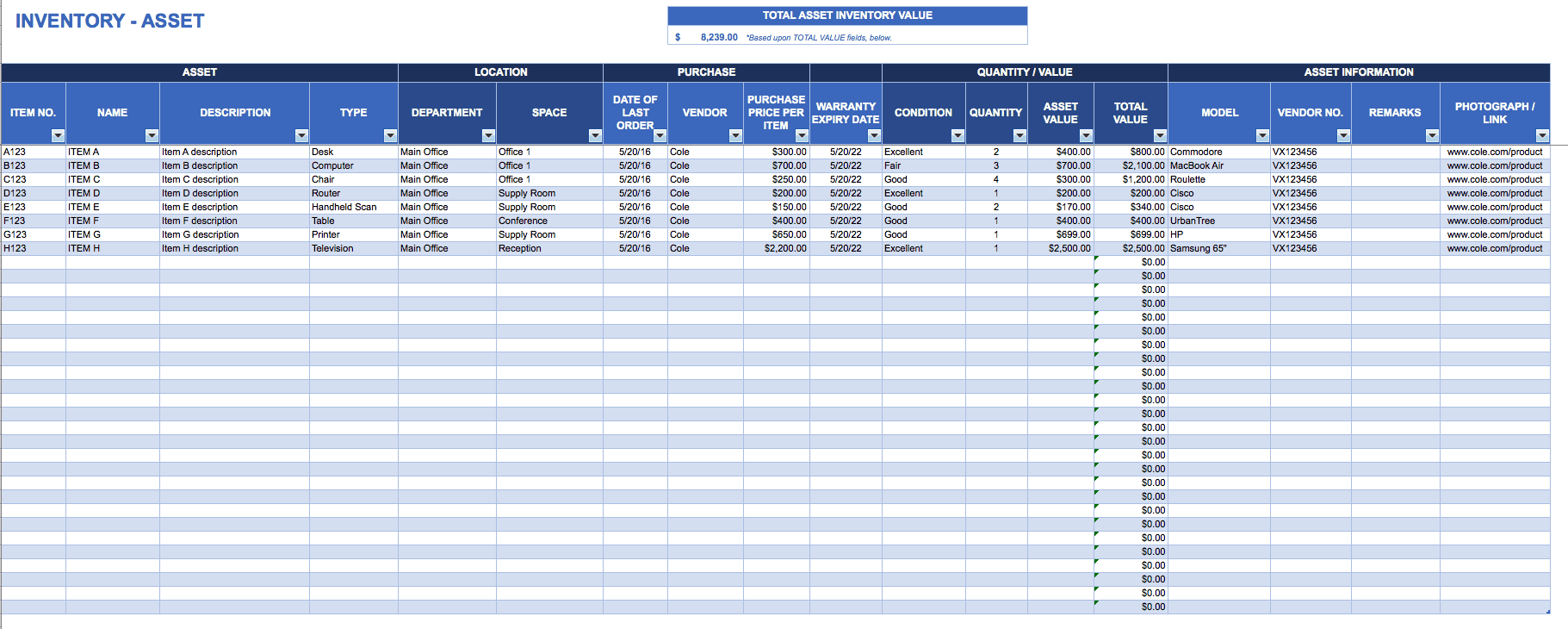
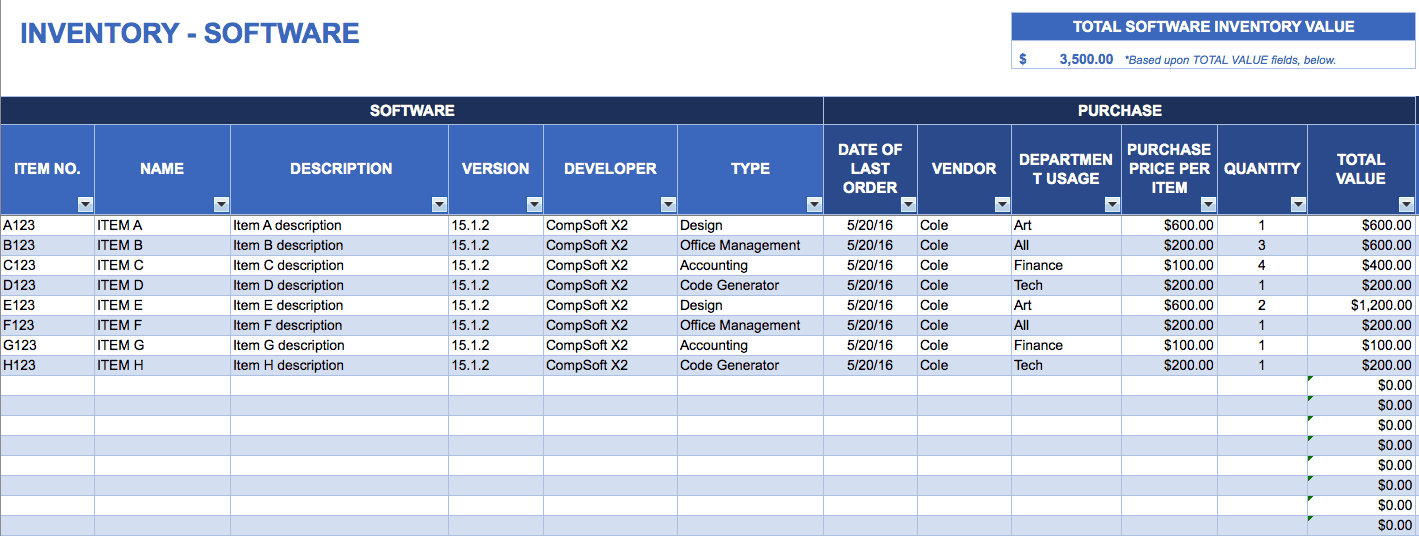
Here are some project management templates that may be a useful tool for the IT Infrastructure Project Manager:
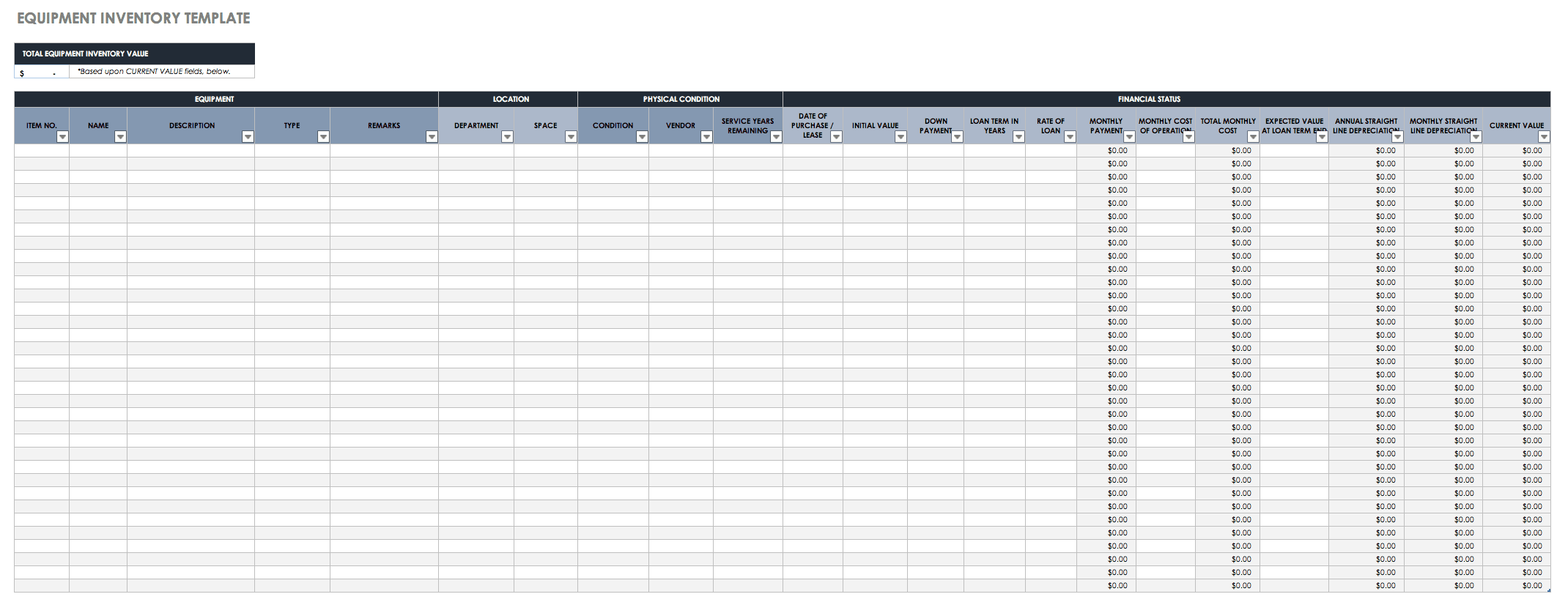
Download Equipment Inventory Template
Download IT Strategic Planning Template
Download Asset Tracking Template
Download Software Inventory Template
How to Choose the Right IT Infrastructure Management Solution
The solutions available today focus on multipurpose functionality to support homogeneous or heterogeneous business environments. Therefore, they stress features like ease of deployment and use, instant insight and views, and predictive proactive monitoring. These software-based systems are also shown to have elements of self-learning that increase industry or company effectiveness.
Before choosing a solution, IT management staff must first define the services, controls, and reporting that are both required and desired to enhance operations - before calling in vendors for demonstrations. Many of today’s tools have scalable systems that provide onsite and remote capabilities for physical and virtual management, support industry-specific protocols, and include dashboards from vendors who offer training, consulting, and enhanced services. Remember, the solution you choose must address your unique business needs. For more complex aspects of the solution decision-making process, evaluate the following functional areas:
- Infrastructure lifecycle management (the lifecycle of an infrastructure asset from planning, through operation, and disposal or end-of-life)
- Capacity optimization and resource forecasting
- Granular monitoring and troubleshooting of physical and virtual assets (VM)
- Network monitoring of the entire infrastructure, including routers, switches, VPNs, firewalls, appliances, etc.
- Resource allocation
- Trend analysis and reporting across multiple data sources
- Threshold value alerting, triggers, and remediation
- Ability to “self-learn” to enhance operational functions
- Heterogeneous environment support, including virtual and cloud
- Communication and support for Amazon Web Services (AWS), Google, and Microsoft Azure
- Support for industry standard protocols, such as WMI and SMTP
- Remote and mobile access
- Network security functions
- Automation
- Detection of problematic resources and perform preventative action
- Network utilization and system health checks
- Support for common services such as Active Directory and Microsoft Exchange
Additionally, many vendors tout ease of deployment, seamless integration, and real-time views into infrastructures that have multiple platforms, providers, and equipment. There are numerous offerings from vendors including Hewlett-Packard, IBM, BMC, Microsoft, and CA Technologies. Some vendors work to integrate legacy or acquired technologies into a single-solution approach.
Benefits of IT Infrastructure Management
The benefits of IT infrastructure management solutions all stem from the ease of operation, clarity of information and reporting, and cost savings. Behavior that supports these outcomes include:
- Rapid response to changing and disruptive conditions
- Flexible and agile procedures that lead to proactive (rather than reactive) management strategies
- Automated work reduces labor, costs, and impactful events and incidents, allows better capacity planning, centralizes information, and provides near real-time information and reporting
- Streamlined day-to-day functions and operations free up time for personnel so they can better plan for and meet demands of overall business strategy, including scaling for competitive growth
- Improved customer satisfaction and overall performance
- Reduced downtime by accelerating deployments and decreasing repair time
Although IT infrastructure management is implemented to simplify processes, it can also be disruptive, especially in the initial deployment. CIOs and CTOs are tasked to adapt within the constraints of their budgets and skills of their staff to “move at the speed of the enterprise” and quickly adopt, deploy, and manage new systems and processes - sometimes at the detriment of adequate planning and research.
Business user requirements and consumer expectations for reliable IT services continue to grow. With these demands, the landscape of IT services and its management continues to become more complex and larger in scope. The need for simple solutions, clear reporting, real-time views, secure systems, cost-saving functionality, scalability, mobility, and reliability will also continue to grow. The promise from vendors, such as ease of deployment, day-to-day functionality, multi-tiered reporting, security enhancements, and capacity optimization also extend to the ability to go from “putting out fires” to proactive management strategies that leverage technology, data, and information for competitive growth.
IT Infrastructure Management for Healthcare
IT infrastructure management is a valuable resource that can be leveraged in healthcare organizations to monitor, manage, and effectively leverage facilities, IT assets, networks, security systems, and various other processes in one centralized location. IT infrastructure management in a healthcare organization offers a way to track, manage, and store resources, operations and process information, and protected health information (PHI).
While healthcare organizations can benefit from the visible and collaborative benefits that this sort of infrastructure management provides, they must also abide by stringent security, data protection, and compliance standards, such as HIPAA. To reap the benefits of centralized IT systems management while also remaining compliant to security standards, you need a powerful, real-time, and secure tool to run your systems.
Smartsheet is a work execution platform that enables healthcare companies to improve work efficiency, scale business processes, and securely manage and store PHI, while meeting or exceeding all of HIPAA’s regulatory requirements. Streamline reporting and organize all necessary information in one centralized location to ensure your IT operations and systems run efficiently.
Interested in learning more about how Smartsheet can help you maximize your efforts? Discover Smartsheet for Healthcare.
IT Infrastructure Management in the News
The cloud, Internet of Things (IoT), and mobility have and will continue to impact business operations. Simultaneously, the movement to the cloud is causing IT staff to evolve and plan for useful, adaptive, and scalable infrastructure management solutions. As enterprises move IT infrastructure to cloud-based systems, purchasing tools to support this transition will depend on a variety of cloud-specific elements, including whether the cloud is private, public (such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure), or a hybrid mix. The new IoT management suite provided by VMware expands the traditional datacenter infrastructure management to include cloud, mobile, and IoT.
It is no surprise that this unique and growing challenge associated with IT infrastructure management, IoT, and cloud are main topics at Gartner Research’s IT Infrastructure and Operations Management Summit in 2017. As Gartner literature on the event explains, “Transformation requires a solid foundation from which to drive and deliver sustained business value.” To that end, the three-day agenda for the event is packed with seminars on cloud solutions, technology trends, and harnessing the IoT, to both educate and dispel “outdated beliefs and practices” when adopting or enhancing IT infrastructure practices and management.
Looking toward the future of integrated infrastructure management services and solutions, the trend continues towards the adoption of private, public, and hybrid cloud offerings to build new infrastructures, enhance current capabilities, or integrate with legacy systems. Industry analysts at Gartner Research predict an 18 percent growth in the global public service cloud market, and forecast that expenditures for 2017 will reach almost $250 billion.
A Better Way to Manage IT Infrastructure and Operations with Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.